Test per l'ADHD: Differenze con l'Autismo e Quando Fare uno Screening
Navigare il mondo della neurodivergenza può essere confuso, soprattutto quando i sintomi sembrano sovrapporsi. Potresti ritrovarti a lottare con la concentrazione, le interazioni sociali o emozioni intense e chiederti quale sia la causa. Questo spesso porta a una domanda comune e importante: I miei sintomi sono segni di ADHD, Autismo o entrambi?
Non sei solo in questa incertezza. L'ADHD (Disturbo da Deficit di Attenzione/Iperattività) e il Disturbo dello Spettro Autistico (ASD) sono condizioni del neurosviluppo distinte. Condividono tratti che sfumano i confini. Spesso serve una guida professionale per chiarirli. Comprendere le loro differenze chiave è il primo passo verso la chiarezza e il supporto adeguato.
Questa guida ti aiuterà a decifrare le sfumature tra ADHD e Autismo. Esploreremo i sintomi comuni, evidenzieremo le differenze cruciali e spiegheremo come un primo screening possa essere uno strumento prezioso. Se cerchi un punto di partenza, un test gratuito online può offrire spunti iniziali su potenziali tratti dell'ADHD in modo privato e accessibile.
Comprendere la Sovrapposizione: Perché ADHD e Autismo Vengono Spesso Confusi
Perché ADHD e Autismo vengono così spesso confusi? La ragione principale è il loro impatto condiviso sulle funzioni esecutive. Queste sono le abilità mentali che includono memoria di lavoro, pensiero flessibile e autocontrollo. Ciò crea una somiglianza superficiale nel modo in cui le persone affrontano la vita quotidiana, la scuola e il lavoro.
Tratti Comuni: Disattenzione, Iperattività e Segnali Sociali
In superficie, certi comportamenti possono sembrare quasi identici. Qualcuno con entrambe le condizioni potrebbe avere difficoltà in situazioni sociali o a concentrarsi in un ufficio affollato. Esaminiamo queste caratteristiche condivise:
-
Disattenzione: Un bambino in classe che sogna a occhi aperti e non segue la lezione potrebbe avere ADHD (distratto da stimoli interni o esterni) o Autismo (profondamente assorto nei propri pensieri o in un interesse specifico).
-
Iperattività e Irrequietezza: Movimenti agitati, irrequietezza o movimento costante possono essere segni di iperattività nell'ADHD. Possono anche essere una forma di "stimming" (comportamento auto-stimolante) negli autistici, che aiuta a regolare input sensoriali o emozioni.
-
Difficoltà Sociali: Sia le persone con ADHD che con Autismo possono trovare difficile fare o mantenere amicizie. Potrebbero non cogliere i segnali o avere problemi nel flusso della conversazione. Ma le cause profonde? Totalmente diverse per ADHD vs Autismo.

Le Radici della Confusione: Somiglianze nella Manifestazione Durante la Vita
La confusione non riguarda solo i sintomi; riguarda come si manifestano in diverse fasi della vita. Un bambino piccolo con frequenti scoppi d'ira potrebbe sperimentare la disregolazione emotiva dell'ADHD o il sovraccarico sensoriale legato all'Autismo.
Inoltre, è possibile che qualcuno abbia sia ADHD che Autismo. Questa doppia diagnosi significa che una persona affronta le sfide distinte di entrambe le condizioni simultaneamente. Ciò rende una distinzione netta ancora più complessa e sottolinea la necessità di una valutazione attenta e sfumata.
ADHD vs Autismo: Decifrare le Differenze Chiave nei Sintomi Centrali
Nonostante la sovrapposizione significativa, le motivazioni centrali e le esperienze interne dietro i comportamenti sono fondamentalmente diverse. Comprendere queste distinzioni è la chiave per ottenere una reale consapevolezza.
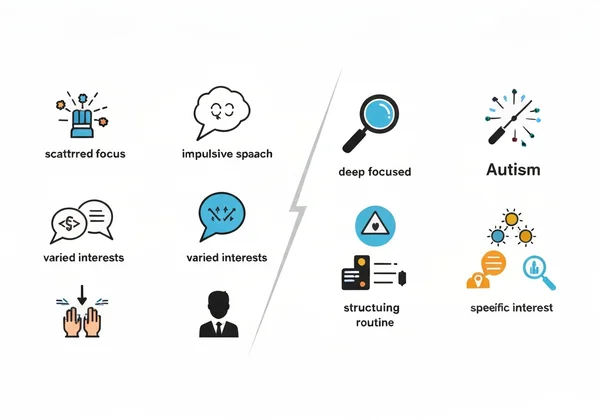
Distinguere l'Interazione Sociale: Diversi Modi di Connettersi
Questa è una delle aree di differenza più significative.
- ADHD: Le difficoltà sociali spesso derivano da impulsività, disattenzione e disregolazione emotiva. Una persona con ADHD potrebbe interrompere gli altri, parlare eccessivamente o perdere parti di una conversazione perché ha perso il filo. Generalmente comprende le regole sociali intuitivamente ma fatica ad applicarle costantemente a causa dei sintomi.
- Autismo: Le sfide sociali sono tipicamente radicate in un modo diverso di elaborare il mondo sociale. Un autistico potrebbe avere difficoltà a comprendere e applicare le norme sociali, interpretare il linguaggio del corpo o capire il sarcasmo. Potrebbe preferire la solitudine o interagire in modi atipici perché motivazione e comprensione sociale sono connesse diversamente.
Attenzione e Concentrazione: da "Non Riesco a Concentrarmi" a "Iperconcentrazione"
Come funziona l'attenzione è un altro differenziatore maggiore.
- ADHD: La concentrazione nell'ADHD è guidata dall'interesse. Compiti noiosi? Difficile mantenerla. Quelli divertenti? Ore di iperfissazione. Regolarla è difficile e gli spostamenti avvengono senza preavviso.
- Autismo: Gli autistici spesso sperimentano "iperconcentrazione" legata ai loro interessi speciali profondi, specifici e spesso a lungo termine. Questa è una concentrazione intensa e profonda che può rendere difficile spostare l'attenzione su altro. A differenza dell'iperfissazione ADHD, questo focus è meno legato alla novità e più a una passione duratura.
Comportamenti Ripetitivi e Interessi Ristretti: Segni Distintivi dello Spettro Autistico
Questa area è un tratto distintivo della diagnosi di Autismo.
- ADHD: Le persone con ADHD prosperano sulla novità e possono passare rapidamente tra hobby e interessi diversi. Il loro comportamento è spesso guidato dalla ricerca di stimoli e può apparire irrequieto o caotico.
- Autismo: Una caratteristica centrale dell'Autismo è la preferenza per routine, prevedibilità e uniformità. Questo può manifestarsi come comportamenti ripetitivi (stimming come sbattere le mani o dondolarsi) e interessi altamente focalizzati e ristretti. Queste routine e interessi forniscono conforto e struttura in un mondo che può sentirsi travolgente.
Regolazione Emotiva: Sfide Uniche per Ogni Condizione
Entrambe le condizioni implicano difficoltà nel gestire le emozioni, ma i fattori scatenanti e le espressioni differiscono.
- ADHD: La disregolazione emotiva è molto comune. Può apparire come frustrazione intensa, impazienza e sbalzi d'umore. Un tratto chiave è la Disforia Sensibile al Rifiuto (RSD), un dolore emotivo estremo in risposta a critiche o rifiuti percepiti.
- Autismo: Le sfide emotive sono spesso collegate a sovraccarico sensoriale, interruzioni della routine o difficoltà nell'identificare ed esprimere sentimenti interni (tratto noto come alessitimia). Uno "squilibrio emotivo" in una persona autistica è una risposta intensa a un completo sovraccarico e non è uguale a un capriccio.
Quando Considerare un Test per l'ADHD per Chiarezza
Se ti riconosci principalmente nelle descrizioni di disattenzione, impulsività e concentrazione incoerente, uno screening ADHD può essere un passo logico e utile.
Chi Beneficia di un Primo Screening ADHD Online?
Uno screening online è un punto di partenza prezioso per molte persone, inclusi:
- Adulti con Dubbi: Se per anni hai sentito di essere disorganizzato, costantemente indietro o incapace di raggiungere il tuo potenziale, esplorare la possibilità di avere l'ADHD potrebbe darti risposte.
- Genitori Preoccupati: Se l'insegnante di tuo figlio segnala problemi di concentrazione, iperattività o controllo degli impulsi in classe, uno screening può aiutarti a organizzare i pensieri prima di parlare con un medico.
- Universitari: Il passaggio all'istruzione superiore spesso espone difficoltà nelle funzioni esecutive precedentemente gestite. Uno screening può aiutare a identificare se l'ADHD è un fattore.
Fare un test ADHD online può aiutarti a vedere se le tue esperienze corrispondono ai tratti consolidati della condizione.

Il Ruolo dello Screening Online: Un Primo Passo Confidenziale Verso la Comprensione
È importante capire cosa sia uno screening online — e cosa non sia. Non è una diagnosi medica. Invece, è uno strumento privato e a bassa pressione progettato per aiutarti a raccogliere informazioni. Basato su domande scientificamente fondate, uno screening fornisce uno sguardo preliminare su potenziali tratti.
I risultati del nostro strumento di screening, come il report alimentato da AI, costruiscono fiducia. Ti danno il linguaggio giusto per una conversazione più produttiva con un professionista sanitario. È un primo passo potenziante nel tuo percorso verso la comprensione.
I Tuoi Prossimi Passi: Oltre lo Screening Online alla Consulenza Professionale
Un risultato di screening online è un pezzo del puzzle, non il quadro finale. La vera chiarezza viene da una valutazione completa da parte di un professionista qualificato che può considerare tutti i fattori.
Prepararsi per una Valutazione Professionale: Cosa Portare dal Tuo Medico
Se decidi di cercare una diagnosi formale, essere preparato può agevolare il processo. Ecco cosa puoi fare:
- Porta il Report dello Screening: Condividi i risultati del tuo autovalutazione ADHD come punto di partenza per la discussione.
- Elenca Esempi Specifici: Scrivi esempi reali di come i tuoi sintomi ti influenzano al lavoro, a casa o nelle relazioni.
- Includi la Tua Storia: Nota eventuali difficoltà ricordate dall'infanzia o dalla scuola, poiché l'ADHD è una condizione che inizia nella prima età.
Perché una Diagnosi Formale è Importante per Supporto e Trattamento
Una diagnosi formale è la porta verso un supporto efficace. Permette ai professionisti sanitari di raccomandare strategie su misura, che possono includere terapia (come la CBT), coaching, accomodamenti lavorativi o farmaci. Convalida le tue esperienze. Fornisce inoltre una struttura chiara per andare avanti e costruire una vita che lavora con il tuo cervello, non contro di esso.
Pronto per Chiarezza? Riconoscere i Tratti ADHD vs Autismo
Ti sei mai chiesto perché la concentrazione vacilla o le chiacchiere sociali sembrano strane? ADHD e Autismo si sovrappongono, ma il "perché" — come l'impulso nell'ADHD vs i bisogni di routine nell'Autismo — ti indirizza verso l'aiuto giusto.
È totalmente normale sentirsi confusi ora. Ma un rapido screening può trasformare quella confusione in chiarezza. Fare quel primo passo per esplorare i tuoi tratti può essere incredibilmente potenziante. Sostituisce l'incertezza con informazioni e ti dà una base per una conversazione più informata sulla tua salute mentale.
Pronto a fare quel primo passo confidenziale? Inizia il tuo test ADHD gratuito oggi e ricevi un report immediato basato su AI per aiutarti nel tuo percorso verso la chiarezza.
Domande Frequenti su ADHD, Autismo e Test
L'ADHD è una forma di Autismo?
No, ADHD e Autismo sono condizioni del neurosviluppo separate e distinte con criteri diagnostici diversi. Tuttavia, possono coesistere e spesso lo fanno, il che significa che una persona può essere diagnosticata con entrambi.
Cosa sembra ADHD ma non lo è?
Diverse condizioni possono avere sintomi che imitano l'ADHD. Queste includono disturbi d'ansia, depressione, mancanza di sonno e disturbi della tiroide. Una valutazione completa da parte di un professionista sanitario è cruciale per differenziarle.
Quali sono i sintomi dell'ADHD?
L'ADHD è caratterizzato da un modello persistente di disattenzione (es. difficoltà a rimanere organizzati, perdere le cose, essere facilmente distratti) e/o iperattività e impulsività (es. agitarsi, parlare eccessivamente, interrompere gli altri).
Si può testare l'ADHD online?
Puoi fare un test di screening affidabile online. Un screening ADHD online è un ottimo strumento per un'autovalutazione preliminare. Aiuta a capire se i sintomi corrispondono ai tratti comuni dell'ADHD ma non fornisce una diagnosi medica.
Cosa devo fare dopo aver fatto un test ADHD online?
Dopo aver fatto un test, esamina il tuo report personalizzato per acquisire consapevolezza sui tuoi tratti. Rifletti su come questi schemi si manifestano nella vita quotidiana. Se i risultati ti risuonano, considera di condividerli con un medico o professionista della salute mentale per discutere i prossimi passi per una valutazione formale.